Unit 7
Unit 7
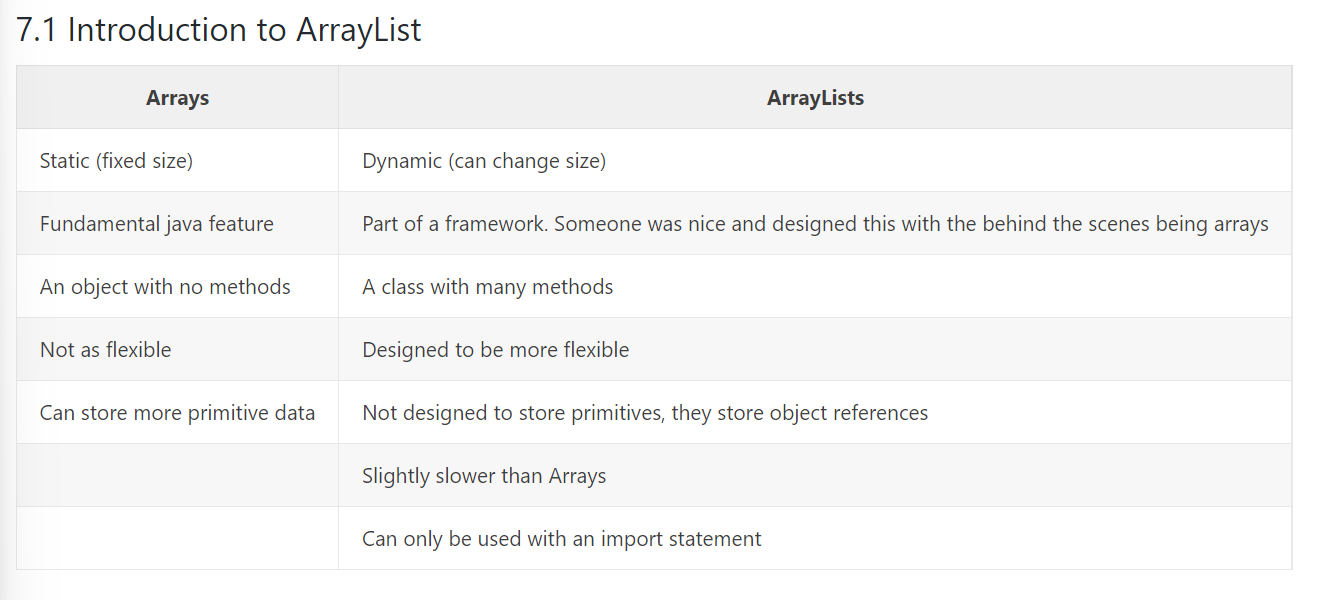
Many methods which can used with arrayLists size(); Returns the number of elements in the list add(obj); Adds element at the end add(index, object); Adds element at specific index remove(index); Removes element from specific index set(index, object);
Example: In dodgeball, the number of people in the game is changing based on who comes in or gets out
Primitive Data Types:
boolean char double int Wrapper Class Data Types (Store the primitive values as objects)
Boolean Character Double Integer
import java.util.ArrayList; //you must import the java.util package
public class introArrayList {
public static void main (String[] args) {
ArrayList When looking at int values, the == operator should be used.
When searching for a double value, we need to make sure the value is close enough by doing some math.
Object instances should always use the .equals(otherThing) method to check for a match.// sum of the elements in the arraylist
ArrayList<Integer> num = new ArrayList<Integer>();
num.add(5);
num.add(1);
num.add(3);
int sum = 0;
for (int number : num) {
sum += number;
}
System.out.println(sum)